Is an abundance of data a boon or a bane for cybersecurity in enterprises?
The impact of data on cybersecurity is a complex issue. Although data can be a useful tool for identifying and averting cyberattacks, improper data management can put security at serious risk. When security teams have too much data to sort through, they may ignore alerts due to alert fatigue, which is caused by data overload. Furthermore, companies that collect more data than they can evaluate and utilize risk the data turning into a liability rather than a resource. Big data can, however, enhance cybersecurity when utilized properly because it offers historical and real-time data that can be used to identify and stop cyberattacks. In general, the relationship between data and cybersecurity is complex, necessitating careful evaluation of the advantages.
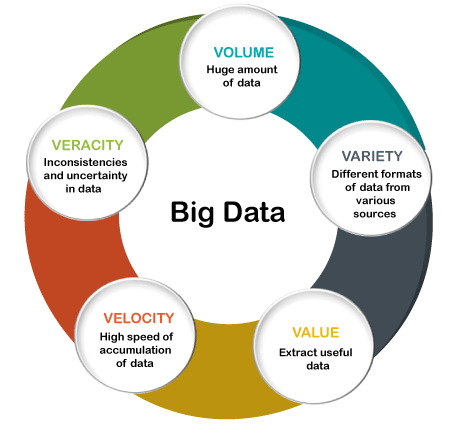
Big data can be a very useful tool for identifying and averting cyberattacks. Businesses can find patterns and anomalies that might point to a breach or attack by analyzing vast amounts of data. To improve cybersecurity, big data analytics, for example, can be used to extract crucial information from large datasets. This is accomplished by developing more effective security threat controls through the analysis of past data. Businesses can now thoroughly analyze historical and current data to determine what is “normal” by fusing big data analytics with machine learning. They then use machine learning to tighten their cybersecurity parameters in light of the findings, enabling them to get alerts whenever there is a deviation from the usual course of events.

Big data and artificial intelligence (AI) combined can be an effective weapon in the fight against cyberthreats. AI systems are able to recognize patterns and anomalies in vast amounts of data that could point to a security breach or attack. To improve cybersecurity, big data analytics, for example, can be used to extract crucial information from large datasets. Businesses can now thoroughly analyze historical and current data to determine what is “normal” by fusing big data analytics with machine learning. They then use machine learning to reinforce their cybersecurity parameters in light of the findings, enabling them to thwart cybersecurity threats by receiving alerts whenever there is a deviation from the usual course of events.
It’s crucial to remember, though, that big data and AI are not a cure-all for cybersecurity problems. There are still a lot of obstacles to be solved, like security and data privacy issues. In order to be held responsible for their decisions, businesses must also make sure that their AI systems are transparent and understandable. The combination of AI and big data has the potential to be a valuable asset in the fight against cyber risks, but it must be used responsibly and ethically.
